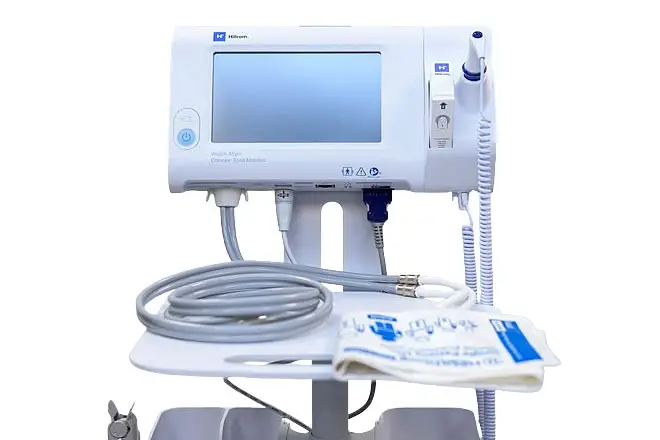
Description
A Vital Signs Monitor is a medical device used to continuously or intermittently measure and display essential physiological parameters of a patient. These parameters typically include:
- Heart Rate (HR): The number of heartbeats per minute, indicating cardiovascular health.
- Blood Pressure (BP): Measures the pressure of blood in the arteries, typically recorded as systolic over diastolic (e.g., 120/80 mmHg).
- Respiratory Rate (RR): The number of breaths taken per minute, important for assessing respiratory function.
- Temperature: Body temperature, often indicating the presence of infection or other medical conditions.
- Oxygen Saturation (SpO2): The percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that is saturated with oxygen, measured using a pulse oximeter.
Key Features:
– Continuous Monitoring: Many monitors provide real-time tracking of vital signs, which is crucial in emergency and intensive care settings.
– Alarms and Alerts: They can alert healthcare providers if vital signs fall outside of preset parameters, allowing for prompt intervention.
– Data Recording: Some monitors store historical data for review and analysis, aiding in diagnosing and tracking patient progress.
– Portability: Many modern vital signs monitors are portable, allowing for use in various settings, including at the bedside, during transport, or in outpatient settings.
Applications:
– Emergency Medicine: Used in hospitals and ambulances to monitor critically ill patients.
– Surgery: Essential for monitoring patients under anesthesia.
– Telemedicine: Increasingly used in remote patient monitoring setups.
– Home Care: Some patients may use home monitoring devices to track their vital signs and report them to healthcare providers.
Types:
- Handheld Monitors: Portable devices used for quick assessments.
- Multi-parameter Monitors: Can track multiple vital signs simultaneously.
- Wearable Monitors: Devices that can be worn on the body, often linked to smartphones or health apps.
Importance:
Monitoring vital signs is crucial for diagnosing health issues, guiding treatment decisions, and assessing a patient’s response to interventions. Regularly tracking these parameters helps healthcare professionals identify trends, predict complications, and ensure timely care.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.