Description
A Diagnostic Cardiology Machine refers to a range of medical devices used to assess and monitor heart function, diagnose heart conditions, and guide treatment. These machines are crucial in cardiology for detecting irregularities in heart rhythms, assessing heart structures, and evaluating the heart’s electrical activity.
Common Types of Diagnostic Cardiology Machines:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) Machine:
– Function: Records the electrical activity of the heart over time. It is the most commonly used cardiology diagnostic tool.
– How it works: Electrodes are placed on the patient’s skin, and the machine captures the heart’s electrical impulses, which are displayed as waves on a screen or printed on paper. It helps diagnose arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other heart conditions.
– Use cases: Diagnosing conditions like atrial fibrillation, ischemia, heart attacks, and monitoring heart health over time.
- Echocardiogram Machine:
– Function: Uses ultrasound waves to create images of the heart’s structures and evaluate its function.
– How it works: A transducer is placed on the chest, and it emits sound waves that bounce off the heart, producing images of the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood flow.
– Use cases: Diagnosing heart valve diseases, cardiomyopathies, pericardial diseases, and assessing heart function in real-time.
- Holter Monitor:
– Function: A portable ECG machine that monitors heart activity over a 24-48 hour period.
– How it works: The patient wears the monitor while going about daily activities, and it continuously records the heart’s electrical activity.
– Use cases: Identifying irregular heart rhythms or arrhythmias that may not show up in a short ECG test, monitoring how heart medications affect heart rhythms.
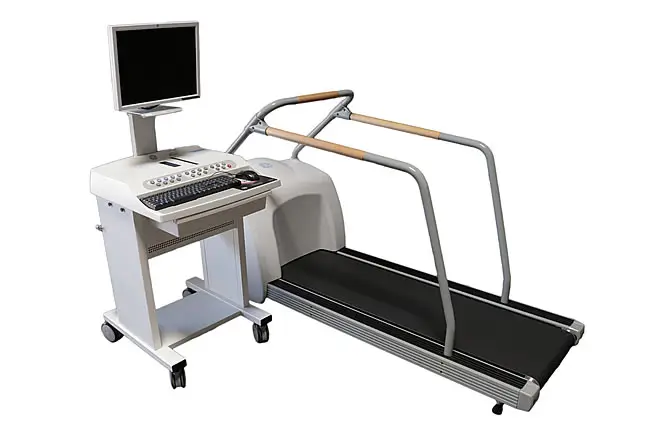
- Stress Test Machine (Treadmill or Exercise ECG):
– Function: Assesses heart function during physical activity, typically exercise.
– How it works: The patient exercises (e.g., walking on a treadmill) while connected to an ECG, and the machine monitors how the heart responds to increasing levels of physical exertion.
– Use cases: Diagnosing coronary artery disease, evaluating exercise tolerance, and assessing the effectiveness of cardiac treatments.
- Cardiac Catheterization Machine (Angiography Machine):
– Function: Provides imaging of the coronary arteries and assesses heart function by inserting a catheter into the heart.
– How it works: A catheter is inserted into a blood vessel and guided to the heart. Dye is injected, and X-ray images are taken to detect blockages or abnormalities in the coronary arteries.
– Use cases: Diagnosing coronary artery disease, assessing heart valve defects, and guiding angioplasty or stent placement.
- Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitor:
– Function: Measures and records blood pressure at regular intervals over 24-48 hours while the patient performs daily activities.
– How it works: The device is worn around the arm, and it automatically inflates to take blood pressure readings at preset intervals.
– Use cases: Diagnosing hypertension (high blood pressure), assessing the effectiveness of blood pressure medications, and identifying white coat syndrome (elevated blood pressure in a clinical setting).
- Event Recorder:
– Function: A portable ECG device similar to a Holter monitor, but the patient manually activates it when symptoms occur.
– How it works: The patient presses a button to record the heart’s electrical activity during symptomatic episodes, like palpitations or dizziness.
– Use cases: Detecting intermittent arrhythmias that don’t happen frequently enough to be captured by a Holter monitor.
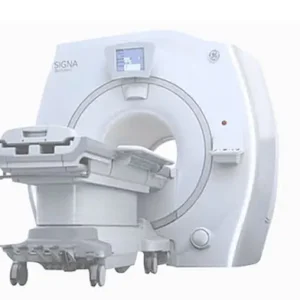
- Cardiac MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging):
– Function: Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the heart’s structure and function.
– How it works: The patient lies in an MRI machine, and detailed images are taken without the use of ionizing radiation.
– Use cases: Diagnosing heart diseases like cardiomyopathy, congenital heart defects, and assessing heart muscle damage after a heart attack.
- Portable Cardiac Ultrasound (Point-of-Care Ultrasound – POCUS):
– Function: A handheld device that provides real-time images of the heart.
– How it works: The physician uses a small ultrasound probe to capture images of the heart on the spot, typically in emergency or urgent care situations.
– Use cases: Rapid assessment of cardiac conditions in emergency rooms or intensive care units (ICUs).
Importance of Diagnostic Cardiology Machines:
These machines help in:
– Early detection of heart diseases, allowing for timely treatment.
– Monitoring the effectiveness of cardiac treatments, like medications or surgeries.
– Preventing severe complications by providing continuous and real-time monitoring of heart conditions.
Advancements in Diagnostic Cardiology:
With advances in technology, many diagnostic cardiology machines are becoming more portable and user-friendly, allowing for easier access to diagnostics in various healthcare settings. Integration with digital health platforms and artificial intelligence (AI) is also improving the accuracy of diagnoses and the ability to track heart health over time.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.