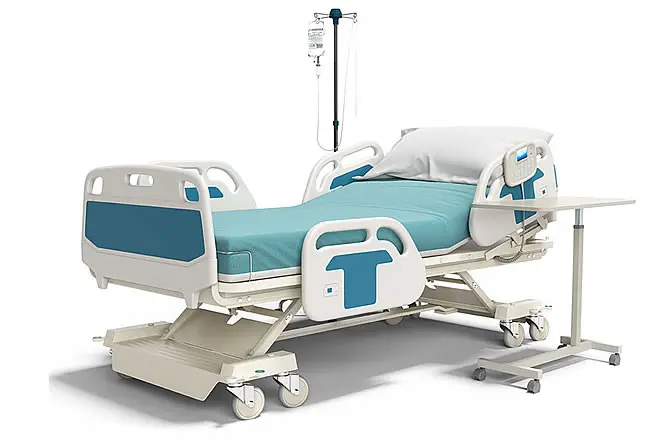
Description
A hospital bed is a specialized bed designed to provide comfort, safety, and mobility for patients in healthcare settings such as hospitals, nursing homes, or private homes. These beds are equipped with various features to support patient care, assist healthcare providers, and enhance recovery. Hospital beds are essential for patient treatment, rehabilitation, and comfort during long-term or critical care situations.
Key Features of Hospital Beds
- Adjustable Height:
– Hospital beds can be raised or lowered to accommodate patient care and mobility. This feature helps patients easily get in and out of bed and allows healthcare workers to provide care at a comfortable height, reducing the risk of injury.
- Adjustable Head, Foot, and Back Sections:
– The bed’s surface can be adjusted into different positions (e.g., sitting up or elevating the legs) to improve patient comfort and help with medical conditions such as breathing difficulties, circulation issues, or postoperative care.
– Fowler’s Position: This is a common position in which the head of the bed is elevated to promote respiratory function and patient comfort.
- Side Rails:
– Safety Rails: Hospital beds typically have adjustable side rails to prevent falls, especially for elderly or disoriented patients. These rails can be raised or lowered and may also serve as supports for getting in and out of bed.
– Half-Rails vs. Full-Rails: Full-length side rails offer maximum protection, while half-rails provide more freedom for movement while still offering support.
- Wheels and Brakes:
– Hospital beds are equipped with caster wheels, allowing them to be easily moved within a room or between rooms. Brakes are installed to lock the bed in place when necessary, ensuring stability during treatment or when the patient is resting.
- Mattress Options:
– Hospital beds often come with specialized mattresses designed to reduce the risk of pressure ulcers (bedsores) in patients who are bedridden for long periods.
– Pressure-Relief Mattresses: These include air or foam mattresses that redistribute weight to prevent pressure sores.
– Alternating Pressure Mattresses: They provide continuous air pressure adjustments to help prevent skin breakdown.
- Electronic Controls:
– Many hospital beds come with electronic controls, allowing patients or caregivers to adjust the bed’s position with ease. Some models include a remote control or buttons on the side rail for convenience.
– Trendelenburg and Reverse Trendelenburg Positions: Some advanced models can tilt the entire bed to position the patient in a head-down or feet-down posture, which can assist in certain medical treatments and circulatory issues.
Types of Hospital Beds
- Manual Hospital Beds:
– These beds require manual cranking or adjustments to change the height or position. They are less expensive but less convenient for patients or caregivers who require frequent adjustments.
- Semi-Electric Hospital Beds:
– Semi-electric beds allow electronic adjustment of the head and foot sections while the bed height is adjusted manually using a hand crank.
- Fully Electric Hospital Beds:
– These beds are entirely controlled via an electronic control system, allowing for easy adjustment of bed height, headrest, footrest, and overall bed positioning. They are the most user-friendly option, often used in hospitals or long-term care facilities.
- Low Beds:
– Designed for patients at high risk of falling, low hospital beds can be adjusted to be very close to the floor, reducing the severity of injuries from falls.
- Bariatric Beds:
– These are specialized hospital beds designed for overweight or obese patients. Bariatric beds are wider and sturdier to support higher weight capacities, and they often come with extra support features to enhance patient safety and comfort.
- ICU Beds:
– Intensive Care Unit (ICU) beds are highly sophisticated, designed for critically ill patients. These beds often come with advanced features such as built-in scales, monitoring systems, and lateral tilt capabilities to help with postural adjustments and patient care.
Common Uses of Hospital Beds
- Patient Recovery:
– Hospital beds are essential for patients recovering from surgery, illness, or injury. Adjustable beds allow for tailored positioning that can help manage pain, breathing, or specific medical needs.
- Long-Term Care:
– For patients in nursing homes or home care settings, hospital beds provide both comfort and safety. They help with mobility and reduce the risk of falls or pressure sores for bedridden patients.
- Critical Care:
– In critical care settings like ICUs, hospital beds support advanced medical equipment and interventions. The ability to adjust a patient’s position can be lifesaving, helping to prevent respiratory complications or facilitate medical procedures.
- Post-Surgical Care:
– Hospital beds provide a supportive environment for post-operative patients who may need frequent position changes to avoid complications such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pneumonia.
Benefits of Hospital Beds
- Improved Patient Comfort:
– The adjustable nature of hospital beds allows patients to find the most comfortable position for resting, eating, or undergoing treatments.
- Safety and Fall Prevention:
– Side rails, height adjustability, and sturdy frames help prevent accidental falls, which is particularly important for elderly or debilitated patients.
- Enhanced Caregiver Access:
– Caregivers can easily position the bed to provide treatments, change bandages, or assist patients without straining themselves, thus reducing the risk of caregiver injury.
- Better Mobility for Patients:
– Patients who are bedridden can adjust their position to improve circulation, reduce the risk of pressure ulcers, and stay more mobile, which is important for overall recovery and well-being.
- Infection Control:
– Many hospital beds are designed with easy-to-clean surfaces and materials, which help in maintaining hygiene and preventing hospital-acquired infections.
Recent Advancements in Hospital Bed Technology
- Smart Beds:
– Some modern hospital beds are equipped with sensors that monitor patient movement, breathing, and weight. These “smart beds” provide real-time data to healthcare providers, helping to prevent falls or detect early signs of patient deterioration.
- Integrated Medical Devices:
– Advanced hospital beds may come with built-in devices like heart monitors, oxygen delivery systems, or adjustable traction mechanisms, allowing for a more integrated approach to patient care.
- Bed Exit Alarms:
– These alarms notify caregivers if a patient is attempting to leave the bed, reducing the risk of falls.
- Temperature Control Mattresses:
– Some hospital beds feature mattresses that can regulate temperature, helping to keep patients comfortable, particularly those with fever or circulatory issues.
Conclusion
Hospital beds play a crucial role in patient care, offering comfort, safety, and enhanced treatment capabilities. They help healthcare providers deliver efficient care, improve patient mobility, and reduce the risk of complications in both short-term and long-term medical settings.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.