Description
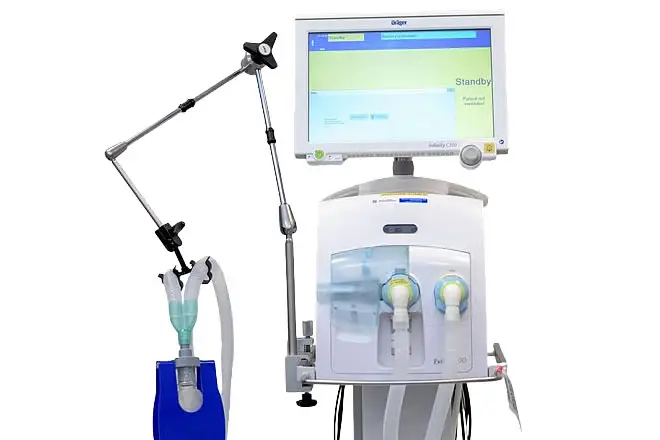
An ICU Ventilator is a critical medical device used in intensive care units (ICUs) to provide mechanical ventilation to patients who are unable to breathe adequately on their own due to severe respiratory conditions or other medical issues. Here are key aspects of ICU ventilators:
Purpose and Function
– Mechanical Ventilation: ICU ventilators assist or fully take over the breathing process for patients with respiratory failure, ensuring that they receive adequate oxygenation and carbon dioxide removal.
– Support During Critical Illness: They are used for patients with conditions like acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations, or after major surgeries.
Key Features
- Modes of Ventilation:
– Assist-Control (AC): Delivers a set number of breaths, but patients can initiate additional breaths.
– Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation (SIMV): Provides a combination of controlled breaths and allows for spontaneous breaths by the patient.
– Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV): Supports spontaneous breathing efforts by providing a preset level of pressure during inhalation.
- Monitoring Capabilities:
– Real-Time Monitoring: ICU ventilators continuously monitor parameters like tidal volume, respiratory rate, airway pressure, and oxygen concentration.
– Alarms: They feature alarms for various conditions, such as high airway pressure, low tidal volume, or changes in patient status, ensuring prompt medical intervention when necessary.
- Adjustable Settings:
– Tidal Volume: The volume of air delivered with each breath can be adjusted based on the patient’s needs.
– FiO2 (Fraction of Inspired Oxygen): The concentration of oxygen delivered can be set to optimize oxygenation.
– PEEP (Positive End-Expiratory Pressure): Maintains a certain level of pressure in the airways at the end of expiration to improve oxygenation and lung compliance.
- Non-invasive and Invasive Options:
– Invasive Ventilation: Involves intubating the patient with an endotracheal tube to connect to the ventilator.
– Non-invasive Ventilation: Uses masks or nasal prongs to deliver positive pressure ventilation without intubation, often used for patients with less severe respiratory failure.
Types of ICU Ventilators
- Conventional Ventilators: Standard ICU ventilators with multiple modes and settings for various patient needs.
- High-Frequency Ventilators: Deliver very rapid, small tidal volumes to maintain oxygenation while minimizing lung injury, often used in specialized cases.
- Portable Ventilators: Smaller, transportable units used for patient transfer or in emergency situations.
Importance in Critical Care
– Life-Saving: ICU ventilators play a vital role in managing patients with severe respiratory failure, allowing them time to recover while providing adequate ventilation and oxygenation.
– Facilitate Weaning: They assist in the gradual process of weaning patients off mechanical support as their respiratory function improves.
– Multidisciplinary Care: ICU ventilators are often used in conjunction with other treatments and monitoring devices in a multidisciplinary approach to critical care management.
Trends and Innovations
– Smart Ventilation: Advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence are increasingly integrated into ICU ventilators to optimize settings and improve patient outcomes.
– Telemedicine Integration: Remote monitoring capabilities allow healthcare providers to manage ventilator settings and monitor patient status from a distance, enhancing care in resource-limited settings.
ICU ventilators are crucial for supporting patients in critical conditions, providing life-sustaining therapy, and enabling recovery from severe respiratory issues.




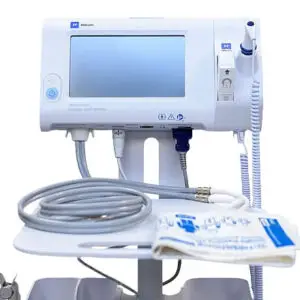
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.