Description
Medical Imaging Machines are essential tools in modern healthcare, used to visualize the internal structures of the body for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. They help healthcare providers diagnose diseases, assess the progression of conditions, and guide treatment decisions. Here are some common types of medical imaging machines and their functions:
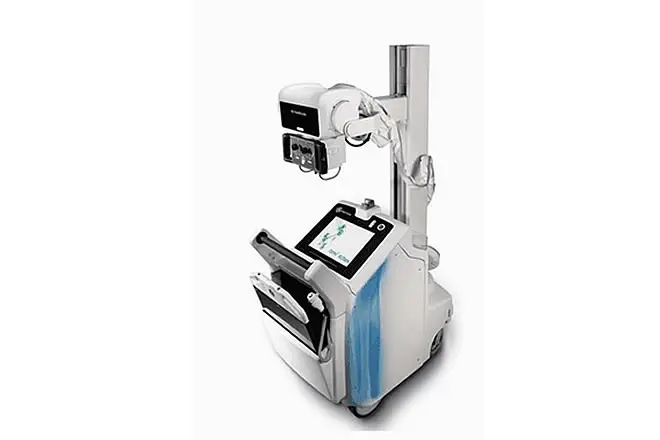
- X-ray Machines
– Function: Use ionizing radiation to produce images of the body’s internal structures, particularly bones.
– Uses: Commonly used to diagnose fractures, infections, and conditions like pneumonia. Specialized types include mammography for breast imaging and fluoroscopy for real-time imaging of movement (e.g., swallowing studies).
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scanners
– Function: Combine multiple X-ray images taken from different angles to create cross-sectional images (slices) of the body.
– Uses: Useful for visualizing complex structures, such as the brain, chest, abdomen, and pelvis. It can help diagnose tumors, internal injuries, and bleeding.
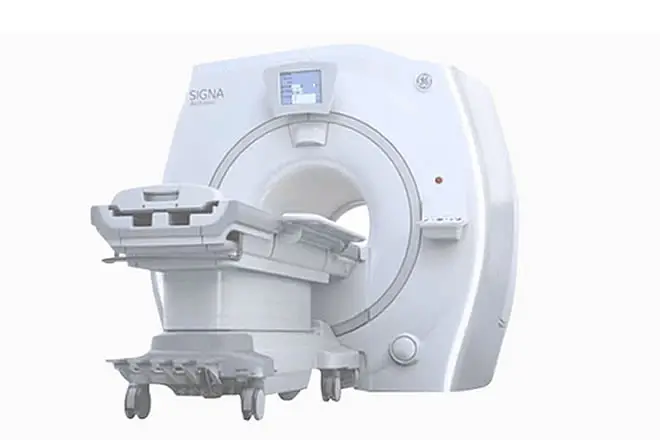
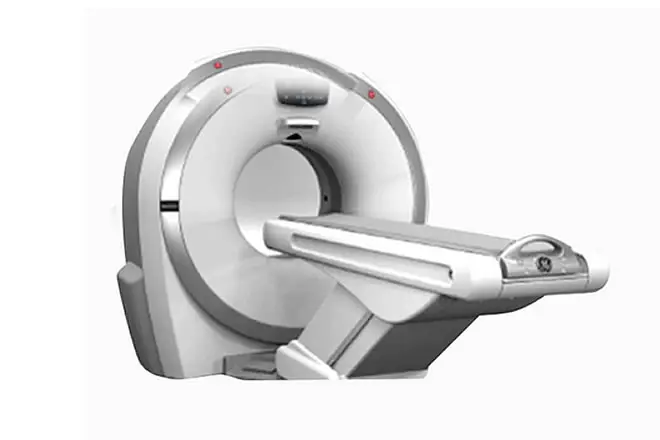
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Machines
– Function: Use strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of soft tissues and organs.
– Uses: Particularly effective for imaging the brain, spinal cord, joints, and soft tissues. MRI is non-invasive and does not use ionizing radiation.
- Ultrasound Machines
– Function: Use high-frequency sound waves to create images of the body’s internal structures.
– Uses: Commonly used in obstetrics to monitor fetal development, as well as for imaging organs like the heart, liver, kidneys, and gallbladder. It’s safe, portable, and does not involve radiation.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scanners
– Function: Use radioactive tracers to visualize metabolic processes in the body.
– Uses: Often used in oncology to detect cancer, assess treatment effectiveness, and evaluate brain function.
- Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT)
– Function: Similar to PET, SPECT uses radioactive substances and a special camera to create 3D images of how blood flows to tissues and organs.
– Uses: Commonly used in cardiology to evaluate heart function and detect abnormalities.
- Fluoroscopy Machines
– Function: Provide real-time imaging using X-rays to visualize the movement of internal structures.
– Uses: Often used during procedures such as barium swallows, catheter placements, or in orthopedic surgery to guide instruments.
Importance in Healthcare
– Diagnosis: Medical imaging is crucial for accurately diagnosing conditions, guiding treatment plans, and monitoring progress.
– Non-invasive: Many imaging techniques are non-invasive, reducing the need for exploratory surgeries.
– Early Detection: Advanced imaging can lead to early detection of diseases, improving treatment outcomes and survival rates.
Trends and Innovations
– Digital Imaging: Transition from film-based to digital imaging has improved image quality and accessibility, allowing for easier storage and sharing of images.
– Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI and machine learning are increasingly being integrated into imaging systems to enhance image analysis, reduce interpretation errors, and aid in diagnostics.
– Portable Imaging: Development of portable imaging technologies, such as handheld ultrasound devices, has improved access to diagnostic imaging in various settings, including remote areas and emergency situations.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.